28 Repository Access Using Protocols
You can access Oracle XML DB Repository data using protocols FTP and HTTP(S)/WebDAV.
28.1 Overview of Oracle XML DB Protocol Server
Oracle XML DB also provides the Oracle XML DB protocol server. This supports standard Internet protocols, FTP, WebDAV, and HTTP(S), for accessing its hierarchical repository or file system. HTTPS provides secure access to Oracle XML DB Repository.
These protocols can provide direct access to Oracle XML DB for many users without having to install additional software. The user names and passwords to be used with the protocols are the same as those for SQL*Plus. Enterprise users are also supported. Database administrators can use these protocols and resource APIs such as DBMS_XDB_REPOS to access Oracle Automatic Storage Management (Oracle ASM) files and folders in the repository virtual folder /sys/asm.
As described in Getting Started with Oracle XML DB and Access to Oracle XML DB Repository Data, Oracle XML DB Repository provides a hierarchical data repository in the database, designed for XML. Oracle XML DB Repository maps path names (or URLs) onto database objects of XMLType and provides management facilities for these objects.
See Also:
Access to Oracle XML DB Repository Data for more information about accessing repository information, and restrictions on that access
Note:
-
When accessing virtual folder
/sys/asmusing Oracle XML DB protocols, you must log in with the privileges of roleDBAbut as a user other thanSYS. -
Oracle XML DB protocols are not supported on EBCDIC platforms.
28.1.1 Session Pooling
Oracle XML DB protocol server maintains a shared pool of sessions. Each protocol connection is associated with one session from this pool. After a connection is closed the session is put back into the shared pool and can be used to serve later connections.
Session pooling improves performance of HTTP(S) by avoiding the cost of re-creating session states, especially when using HTTP 1.0, which creates new connections for each request. For example, a couple of small files can be retrieved by an existing HTTP/1.1 connection in the time necessary to create a database session. You can tune the number of sessions in the pool by setting session-pool-size in the Oracle XML DB configuration file, xdbconfig.xml, or disable it by setting pool size to zero.
Session pooling can affect users writing Java servlets, because other users can see session state initialized by another request for a different user. Hence, servlet writers should only use session memory, such as Java static variables, to hold data for the entire application rather than for a particular user. State for each user must be stored in the database or in a lookup table, rather than assuming that a session only exists for a single user.
Figure 28-1 illustrates the Oracle XML DB protocol server components and how they are used to access files in Oracle XML DB Repository and other data. Only the relevant components of the repository are shown
Figure 28-1 Oracle XML DB Architecture: Protocol Server
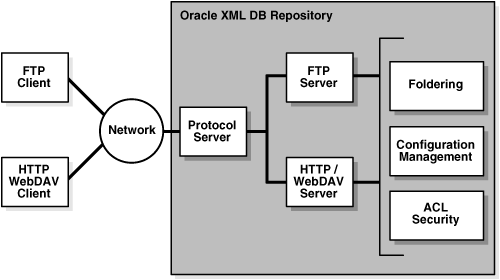
Description of "Figure 28-1 Oracle XML DB Architecture: Protocol Server "
28.2 Oracle XML DB Protocol Server Configuration Management
Oracle XML DB protocol server uses configuration parameters stored in file xdbconfig.xml to initialize its startup state and manage session level configuration. The session pool size and timeout parameters cannot be changed dynamically, that is, you must restart the database in order for these changes to take effect.
28.2.1 Protocol Server Configuration Parameters
The Oracle XML DB protocol configuration parameters are described. They include those common to all protocols, those specific to FTP, and those specific to HTTP(S)/WebDAV.
Table 28-1 shows the parameters common to all protocols. All of their parameter names, except those starting with /xdbconfig, are relative to the following XPath in the Oracle XML DB configuration schema:
/xdbconfig/sysconfig/protocolconfig/common
-
FTP-specific parameters – Table 28-2 shows the FTP-specific parameters. These are relative to the following XPath in the Oracle XML DB configuration schema:
/xdbconfig/sysconfig/protocolconfig/ftpconfig
-
HTTP(S)/WebDAV specific parameters, except servlet-related parameters – Table 28-3 shows the HTTP(S)/WebDAV-specific parameters. These parameters are relative to the following XPath in the Oracle XML DB configuration schema:
/xdbconfig/sysconfig/protocolconfig/httpconfig
See Also:
-
Administration of Oracle XML DB for more information about the configuration file
xdbconfig.xml -
Configuration of Mappings from Default Namespace to Schema Location for more information about the
schemaLocation-mappingsparameter -
Configuration of XML File Extensions for more information about the
xml-extensionsparameter
For examples of the usage of these parameters, see the configuration file, xdbconfig.xml.
Table 28-1 Common Protocol Configuration Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Specifies the mapping of file extensions to mime types. When a resource is stored in Oracle XML DB Repository, and its mime type is not specified, this list of mappings is used to set its mime type. |
|
|
Specifies the mapping of file extensions to languages. When a resource is stored in Oracle XML DB Repository, and its language is not specified, this list of mappings is used to set its language. |
|
|
Specifies the mapping of file extensions to encodings. When a resource is stored in Oracle XML DB Repository, and its encoding is not specified, this list of mappings is used to set its encoding. |
|
|
Specifies the list of filename extensions that are treated as XML content by Oracle XML DB. |
|
|
Maximum number of sessions that are kept in the protocol server session pool |
|
|
If a connection is idle for this time (in hundredths of a second), then the shared server serving the connection is freed up to serve other connections. |
|
|
Time (in hundredths of a second) after which a session (and consequently the corresponding connection) is terminated by the protocol server if the connection has been idle for that time. This parameter is used only if the specific protocol session timeout is not present in the configuration |
|
|
Specifies the default schema location for a given namespace. This is used if the instance XML document does not contain an explicit |
|
|
Time period after which a WebDAV lock on a resource becomes invalid. This could be overridden by a Timeout specified by the client that locks the resource. |
Table 28-2 Configuration Parameters Specific to FTP
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Size of the buffer, in bytes, used to read data from the network during an FTP |
|
|
Port on which FTP server listens. By default, this is |
|
|
Protocol over which the FTP server runs. By default, this is |
|
|
A user-defined welcome message that is displayed whenever an FTP client connects to the server. If this parameter is empty or missing, then the following default welcome message is displayed: "Unauthorized use of this FTP server is prohibited and may be subject to civil and criminal prosecution." |
|
|
Name used to access the host system. The value can be an IP address or a name that is mapped to an IP address using host naming (e.g., in file |
|
|
Time (in hundredths of a second) after which an FTP connection is terminated by the protocol server if the connection has been idle for that time. |
Table 28-3 Configuration Parameters Specific to HTTP(S)/WebDAV (Except Servlet)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Port on which the HTTP(S)/WebDAV server listens, using protocol This parameter must be present, whether or not it is empty. Otherwise, validation of |
|
|
Port on which the HTTP(S)/WebDAV server listens, using protocol This parameter is optional, but, if present, then |
|
|
Protocol over which the HTTP(S)/WebDAV server runs on port This parameter must be present. Otherwise, validation of |
|
|
Protocol over which the HTTP(S)/WebDAV server runs on port This parameter is optional, but, if present, then |
|
|
Time (in hundredths of a second) after which an HTTP(S) session (and consequently the corresponding connection) is terminated by the protocol server if the connection has been idle for that time. |
|
|
Maximum size (in bytes) of an HTTP(S) header |
|
|
Maximum size (in bytes) of an HTTP(S) request body |
|
|
List of filenames that are considered welcome files. When an HTTP(S) |
|
|
The character set in which an HTTP(S) protocol server assumes incoming URL is encoded when it is not encoded in UTF-8 or the Content-Type field Charset parameter of the request. |
|
|
Indication of whether or not anonymous HTTP access to Oracle XML DB Repository data is allowed using an unlocked |
|
|
The HTTP authentication mechanisms allowed. See Configuration and Management of Authentication Mechanisms for HTTP |
|
|
HTTP header that specifies the expiration date and time for a URL. See Control of URL Expiration Time. |
Note:
Oracle recommends that you use the subprograms of PL/SQL package DBMS_XDB_CONFIG to set or change FTP or HTTP port numbers. Do not set ports by directly editing configuration file xdbconfig.xml
28.2.2 Configuring Secure HTTP (HTTPS)
To enable the repository to use secure HTTP connections (HTTPS), a database administrator (DBA) must configure the database accordingly: configure parameters http2-port and http2-protocol, enable the HTTP Listener to use SSL, and enable launching of the TCPS Dispatcher. The DBA must then stop and restart the database and the listener.
See Also:
Configuration of Oracle XML DB Using xdbconfig.xml for information about configuring Oracle XML DB parameters
28.2.2.1 Enabling the HTTP Listener to Use SSL
To configure the HTTP Listener for SSL, a database administrator (DBA) must create a wallet for the server and import a certificate; specify the wallet location to the server; disable client authentication; add an SSL_DH_anon cipher suite to SSL_CIPHER_SUITES; and create a listening end point that uses TCP/IP with SSL.
More precisely, a DBA must carry out the following steps to configure the HTTP Listener for SSL.
-
Create a wallet for the server and import a certificate – Use Oracle Wallet Manager to do the following:
-
Create a wallet for the server.
-
If a valid certificate with distinguished name (DN) of the server is not available, create a certificate request and submit it to a certificate authority. Obtain a valid certificate from the authority.
-
Import a valid certificate with the distinguished name (DN) of the server into the server.
-
Save the new wallet in obfuscated form, so that it can be opened without a password.
See Also:
Oracle Database Enterprise User Security Administrator's Guide for information about how to create a wallet
-
-
Specify the wallet location to the server – Use Oracle Net Manager to do this. Ensure that the configuration is saved to disk. This step updates files
sqlnet.oraandlistener.ora. -
Disable client authentication at the server, since most Web clients do not have certificates. Use Oracle Net Manager to do this. This step updates file
sqlnet.ora. -
Add an
SSL_DH_anoncipher suite toSSL_CIPHER_SUITES– Use any of these:-
SSL_DH_anon_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA -
SSL_DH_anon_WITH_RC4_128_MD5 -
SSL_DH_anon_WITH_DES_CBC_SHA
This step updates file
sqlnet.ora. -
-
Create a listening end point that uses TCP/IP with SSL – Use Oracle Net Manager to do this. This step updates file
listener.ora.
See Also:
Oracle Database Security Guide for detailed information regarding steps 1 through 5
28.2.2.2 Enabling TCPS Dispatcher
To enable launching of a TCPS dispatcher during database startup, a database administrator (DBA) must edit the database pfile.
The following line must be added to the pfile, where SID is the SID of the database:
dispatchers=(protocol=tcps)(service=SIDxdb)
The database pfile location depends on your operating system, as follows:
-
MS Windows –
PARENT/admin/orcl/pfile, wherePARENTis the parent folder of folderORACLE_HOME -
UNIX, Linux –
$ORACLE_HOME/admin/$ORACLE_SID/pfile
28.2.3 Using Listener Status to Check Port Configuration
You can use the TNS Listener command, lsnrctl status, to verify that HTTP(S) and FTP support has been enabled. An example illustrates this.
See Also:
Example 28-1 Listener Status with FTP and HTTP(S) Protocol Support Enabled
LSNRCTL for 32-bit Windows: Version 11.1.0.5.0 - Production on 20-AUG-2007 16:02:34
Copyright (c) 1991, 2007, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Connecting to (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=IPC)(KEY=EXTPROC1521))) STATUS of the LISTENER
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Alias LISTENER
Version TNSLSNR for 32-bit Windows: Version 11.1.0.5.0 - Beta
Start Date 20-JUN-2007 15:35:40
Uptime 0 days 16 hr. 47 min. 42 sec
Trace Level off
Security ON: Local OS Authentication
SNMP OFF
Listener Parameter File C:\oracle\product\11.1.0\db_1\network\admin\listener.ora
Listener Log File c:\oracle\diag\tnslsnr\quine-pc\listener\alert\log.xml
Listening Endpoints Summary...
(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=ipc)(PIPENAME=\\.\pipe\EXTPROC1521ipc)))
(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=quine-pc.example.com)(PORT=1521)))
(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=quine-pc.example.com)
(PORT=21))(Presentation=FTP)(Session=RAW))
(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=quine-pc.example.com)
(PORT=443))(Presentation=HTTP)(Session=RAW))
Services Summary...
Service "orcl.example.com" has 1 instance(s).
Instance "orcl", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service...
Service "orclXDB.example.com" has 1 instance(s).
Instance "orcl", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service...
Service "orcl_XPT.example.com" has 1 instance(s).
Instance "orcl", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service...
The command completed successfully
28.2.4 Configuring Protocol Port Parameters after Database Consolidation
In a multitenant container database (CDB), protocol server port numbers distinguish the plugged-in pluggable databases (PDBs): each such database must have unique port numbers. A database administrator (DBA) must ensure that each port number used by a PDB is unique.
To avoid port conflicts and to resolve any port conflicts that might result from consolidation, a database administrator must proceed as follows:
- Use PL/SQL function
DBMS_XDB_CONFIG.usedPortto obtain the port numbers used by the other PDBs in the same CDB. - Use PL/SQL subprogram
DBMS_XDB_CONFIG.setFTPPortorDBMS_XDB_CONFIG.setHTTPPort, as needed, to change each port number that conflicts so that it is unique.
Note:
After a PDB plug-in or clone operation, and until Oracle XML DB has been fully initialized, the port parameter settings in the configuration file, xdbconfig.xml, might be undefined. Oracle recommends that you use DBMS_XDB_CONFIG subprogram getFTPPort, getHTTPPort, getHTTPSPort, setFTPPort, setHTTPPort, or setHTTPSPort to obtain or modify a port value.
28.2.5 Configuration and Management of Authentication Mechanisms for HTTP
You configure the authentication mechanisms to allow for HTTP access to Oracle XML DB Repository by setting element authentication, a child of element httpconfig, in configuration file xdbconfig.xml.
Starting with 12c Release 1 (12.1.0.1), Oracle Database supports not only basic authentication but also digest access authentication.
User credentials are case-sensitive. In particular, to be authenticated, a user name must exactly match the name as it was created (which by default is all uppercase).
Digest access authentication, also known as digest authentication provides encryption of user credentials (name, password, etc.) without the overhead of complete data encryption.
You can configure the authentication mechanism to use by setting element authentication, a child of element httpconfig, in configuration file xdbconfig.xml. Element authentication is optional. If absent then only basic authentication is used.
Element authentication has two possible child elements:
-
Element
allow-mechanismspecifies an allowed mechanism:basic,digest, orcustom. Use a separateallow-mechanismelement to specify each mechanism you want to allow. -
Element
digest-authis optional. It specifies information for a digest mechanism. Its child elementnonce-timeoutspecifies the number of seconds that a given nonce remains valid. The default value is 300 seconds.The default value is used if there is an
allow-mechanismthat specifiesdigestbut there is nodigest-authelement. Adigest-authelement is ignored if there is noallow-mechanismthat specifiesdigest.
HTTP requests are accepted for each allow-mechanism specified. Authentication challenges are presented in the order of the specified allow-mechanism types. For example, if both digest and basic are present, in that order, then a digest challenge is presented before a basic challenge. Oracle recommends that you always put a stronger authentication before a weaker one. (Digest authentication is stronger than basic authentication.)
See Also:
-
Upgrade or Downgrade of an Existing Oracle XML DB Installation for installation, upgrade, and downgrade considerations
-
RFC2617, HTTP Authentication: Basic and Digest Access Authentication,
http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2617
28.2.5.1 Nonces for Digest Authentication
With digest authentication, the server generates a nonce whenever it issues an unauthorized response. Clients include the nonce in requests to the server. The server checks nonces received from the client to see if it needs to refuse the client authentication. A client can authenticate the server the same way.
A nonce is a unique string that the server generates each time it issues an HTTP 401 (unauthorized) response. Clients include the nonce in subsequent requests that they issue to the server. The server checks the nonce it receives from the client. If incorrect or if the nonce-timeout period has expired, the server can immediately refuse to authenticate.
(A client can use the same mechanism to authenticate the server: it can generate its own nonce. Both client and server can use this client nonce to help prevent particular plain-text attacks.)
A new nonce is created each time the server sends a digest challenge to a client. A nonce is based on a nonce key. The initial nonce key is generated randomly when you install or upgrade the database.
If you use digest authentication then Oracle also recommends that you create a new nonce key periodically, to ensure the integrity of the key. You use PL/SQL procedure DBMS_XDB_ADMIN.createNonceKey to do this.
28.2.6 Oracle XML DB Repository and File-System Resources
Protocol specifications, RFC 959 (FTP), RFC 2616 (HTTP), and RFC 2518 (WebDAV) implicitly assume an abstract, hierarchical file system on the server side. This is mapped to Oracle XML DB Repository. The repository provides name resolution, ACL-based security, and an ability to store and retrieve any content.
The repository can store binary data input through FTP and XML schema-based documents.
28.2.7 Protocol Server Handles XML Schema-Based or Non-Schema-Based XML Documents
Oracle XML DB protocol server always checks whether a document being inserted is based on an XML schema that is registered with Oracle XML DB Repository. If it is, then the XMLType storage model to use is determined by that XML schema. If it is not, then the document is stored as a BLOB.
28.3 FTP and the Oracle XML DB Protocol Server
File Transfer Protocol (FTP), specified in RFC959, is one of the oldest and most popular protocols. It provides access to heterogeneous file systems in a uniform manner. You can use FTP to access and update data stored in Oracle XML DB Repository.
28.3.1 Oracle XML DB Protocol Server: FTP Features
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is implemented by dedicated clients at the operating system level, file-system explorer clients, and browsers. FTP is typically session-oriented: a user session is created through an explicit logon, a number of files or directories are downloaded and browsed, and then the connection is closed.
The transfer of command messages and the return of status happens on a single connection. However, a new connection is opened between the client and the server for data transfer. With HTTP(S), by contrast, commands and data are transferred using a single connection.
Note:
For security reasons, FTP is disabled, by default, for Oracle Database. This is because the IETF FTP protocol specification requires that passwords be transmitted in clear text. Disabling is done by configuring the FTP server port as zero (0). To enable FTP, set the ftp-port parameter to the FTP port to use, such as 2100.
See Also:
-
RFC 959: FTP Protocol Specification –
http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc959.txt -
Configuration of Oracle XML DB Using xdbconfig.xml for information about configuring parameters
28.3.1.1 FTP Features That Are Not Supported
FTP features that are not supported by Oracle XML DB include record-oriented files and operations append, allocate, account, and abort.
Oracle XML DB implements FTP, as defined by RFC 959, with the exception of the following optional features:
-
Record-oriented files, for example, only the
FILEstructure of theSTRUmethod is supported. This is the most widely used structure for transfer of files. It is also the default specified by the specification. Structure mount is not supported. -
Append.
-
Allocate. This pre-allocates space before file transfer.
-
Account. This uses the insecure Telnet protocol.
-
Abort.
28.3.1.2 Supported FTP Client Methods
Oracle XML DB supports several FTP client methods for access to Oracle XML DB Repository.
-
cdup– change working directory to parent directory -
cwd– change working directory -
dele– delete file (not directory) -
list,nlst– list files in working directory -
mkd– create directory -
noop– do nothing (but timeout counter on connection is reset) -
pasv,port– establish a TCP data connection -
pwd– get working directory -
quit– close connection and quit FTP session -
retr– retrieve data using an established connection -
rmd– remove directory -
rnfr,rnto– rename file (two-step process: from file, to file) -
stor– store data using an established connection -
syst– get system version -
type– change data type:asciiorimagebinary types only -
user,pass– user login
See Also:
-
FTP Quote Methods for supported FTP
quotemethods -
Using FTP with Oracle ASM Files for an example of using FTP method
proxy
28.3.1.3 FTP Quote Methods
Oracle Database supports several FTP quote methods, which provide information directly to Oracle XML DB.
-
rm_r– Remove file or folder<resource_name>. If a folder, recursively remove all files and folders contained in<resource_name>.quote rm_r <resource_name> -
rm_f – Forcibly remove a resource.quote rm_f <resource_name> -
rm_rf– Combinesrm_randrm_f: Forcibly and recursively removes files and folders.quote rm_rf <resource_name> -
set_nls_locale– Specify the character-set encoding (<charset_name>) to be used for file and directory names in FTP methods (including names in method responses).quote set_nls_locale {<charset_name> | NULL}Only IANA character-set names can be specified for
<charset_name>. Ifnls_localeis set toNULLor is not set, then the database character set is used. -
set_charset– Specify the character set of the data to be sent to the server.quote set_charset {<charset_name> | NULL}The
set_charsetmethod applies to only text files, not binary files, as determined by the file-extension mapping to MIME types that is defined in configuration filexdbconfig.xml.If the parameter provided to
set_charsetis<charset_name>(notNULL), then it specifies the character set of the data.If the parameter provided to
set_charsetisNULL, or if noset_charsetcommand is given, then the MIME type of the data determines the character set for the data.-
If the MIME type is not
text/xml), then the data is not assumed to be XML. The database character set is used. -
If the MIME type is
text/xml, then the data represents an XML document.If a byte order markFoot 1 (BOM) is present in the XML document, then it determines the character set of the data.
If there is no BOM, then:
-
If there is an encoding declaration in the XML document, then it determines the character set of the data.
-
If there is no encoding declaration, then the UTF-8 character set is used.
-
-
28.3.1.4 Uploading Content to Oracle XML DB Repository Using FTP
An example shows the commands issued and the output generated when a standard command line FTP tool loads documents into Oracle XML DB Repository:
The key point demonstrated by Figure 28-3 and Example 28-2 is that neither Windows Explorer nor an FTP tool is aware that it is working with Oracle XML DB. Since such tools and Oracle XML DB both support open Internet protocols they work with each other out of the box.
Any tool that understands the WebDAV or FTP protocol can be used to create content managed by Oracle XML DB Repository. No additional software needs to be installed on the client or the mid-tier.
When the contents of folders are viewed using a tool such as Windows Explorer or FTP, the lengths of any XML Schema-based documents contained in the folder are shown as zero (0) bytes. This was designed as such for two reasons:
-
It is not clear what the size of a document should be. Is it the size of the
CLOBinstance generated by printing the document, or the number of bytes required to store the objects used to persist the document inside the database? -
Regardless of which definition is chosen, calculating and maintaining this information is costly.
Example 28-2 Uploading Content to the Repository Using FTP
$ ftp mdrake-sun 2100
Connected to mdrake-sun.
220 mdrake-sun FTP Server (Oracle XML DB/Oracle Database 10g Enterprise Edition
Release 10.1.0.1.0 - Beta) ready.
Name (mdrake-sun:oracle10): QUINE
331 Password required for QUINE
Password: password
230 QUINE logged in
ftp> cd /source/schemas
250 CWD Command successful
ftp> mkdir PurchaseOrders
257 MKD Command successful
ftp> cd PurchaseOrders
250 CWD Command successful
ftp> mkdir 2002
257 MKD Command successful
ftp> cd 2002
250 CWD Command successful
ftp> mkdir "Apr"
257 MKD Command successful
ftp> put "Apr/AMCEWEN-20021009123336171PDT.xml"
"Apr/AMCEWEN-20021009123336171PDT.xml"
200 PORT Command successful
150 ASCII Data Connection
226 ASCII Transfer Complete
local: Apr/AMCEWEN-20021009123336171PDT.xml remote:
Apr/AMCEWEN-20021009123336171PDT.xml
4718 bytes sent in 0.0017 seconds (2683.41 Kbytes/s)
ftp> put "Apr/AMCEWEN-20021009123336271PDT.xml"
"Apr/AMCEWEN-20021009123336271PDT.xml"
200 PORT Command successful
150 ASCII Data Connection
226 ASCII Transfer Complete
local: Apr/AMCEWEN-20021009123336271PDT.xml remote:
Apr/AMCEWEN-20021009123336271PDT.xml
4800 bytes sent in 0.0014 seconds (3357.81 Kbytes/s)
.....
ftp> cd "Apr"
250 CWD Command successful
ftp> ls -l
200 PORT Command successful
150 ASCII Data Connection
-rw-r--r1 QUINE oracle 0 JUN 24 15:41 AMCEWEN-20021009123336171PDT.xml
-rw-r--r1 QUINE oracle 0 JUN 24 15:41 AMCEWEN-20021009123336271PDT.xml
-rw-r--r1 QUINE oracle 0 JUN 24 15:41 EABEL-20021009123336251PDT.xml
-rw-r--r1 QUINE oracle 0 JUN 24 15:41 PTUCKER-20021009123336191PDT.xml
-rw-r--r1 QUINE oracle 0 JUN 24 15:41 PTUCKER-20021009123336291PDT.xml
-rw-r--r1 QUINE oracle 0 JUN 24 15:41 SBELL-20021009123336231PDT.xml
-rw-r--r1 QUINE oracle 0 JUN 24 15:41 SBELL-20021009123336331PDT.xml
-rw-r--r1 QUINE oracle 0 JUN 24 15:41 SKING-20021009123336321PDT.xml
-rw-r--r1 QUINE oracle 0 JUN 24 15:41 SMCCAIN-20021009123336151PDT.xml
-rw-r--r1 QUINE oracle 0 JUN 24 15:41 SMCCAIN-20021009123336341PDT.xml
-rw-r--r1 QUINE oracle 0 JUN 24 15:41 VJONES-20021009123336301PDT.xml
226 ASCII Transfer Complete
remote: -l
959 bytes received in 0.0027 seconds (349.45 Kbytes/s)
ftp> cd ".."
250 CWD Command successful
....
ftp> quit
221 QUIT Goodbye.
$
28.3.1.5 Using FTP with Oracle ASM Files
Oracle Automatic Storage Management (Oracle ASM) organizes database files into disk groups for simplified management and added benefits such as database mirroring and I/O balancing. You can use protocols and resource APIs to access Oracle ASM files in repository virtual folder /sys/asm. All files in /sys/asm are binary.
Typical uses are listing, copying, moving, creating, and deleting Oracle ASM files and folders. Example 28-3 is an example of navigating the Oracle ASM virtual folder and listing the files in a subfolder.
The structure of the Oracle ASM virtual folder, /sys/asm, is described in Access to Oracle XML DB Repository Data. In Example 28-3, the disk groups are DATA and RECOVERY; the database name is MFG; and the directories created for aliases are dbs and tmp. This example navigates to a subfolder, lists its files, and copies a file to the local file system.
In Example 28-3, after connecting to and logging onto database myhost (first four lines), FTP methods cd and ls are used to navigate and list folders, respectively. When in folder /sys/asm/DATA/dbs, FTP command get is used to copy files t_db1.f and t_ax1.f to the current folder of the local file system. Then, FTP command put is used to copy file my_db2.f from the local file system to folder /sys/asm/DATA/dbs.
Database administrators can copy Oracle Automatic Storage Management (Oracle ASM) files from one database server to another or between the database and a local file system. Example 28-4 shows copying between two databases. For this, the proxy FTP client method can be used, if available. The proxy method provides a direct connection to two different remote FTP servers.
Example 28-4 copies an Oracle ASM file from one database to another. Terms with the suffix 1 correspond to database server1. Terms with the suffix 2 correspond to database server2. Depending on your FTP client, the passwords you type might be echoed on your screen. Take the necessary precautions so that others do not see these passwords.
In Example 28-4:
-
Line 1 opens an FTP control connection to the Oracle XML DB FTP server,
server1. -
Lines 2–4 log the database administrator onto
server1asUSERNAME1. -
Line 5 navigates to
/sys/asm/DATAFILE/MFG/DATAFILEonserver1. -
Line 6 opens an FTP control connection to the second database server,
server2. At this point, the FTP commandproxy ?could be issued to see the available FTP commands on the secondary connection. (This is not shown.) -
Lines 7–9 log the database administrator onto
server2asUSERNAME2. -
Line 10 navigates to
/sys/asm/DATAFILE/MFG/DATAFILEonserver2. -
Line 11 copies Oracle ASM file
dbs2.ffromserver2to Oracle ASM filetmp1.fonserver1. -
Line 12 copies Oracle ASM file
dbs1.ffromserver1to Oracle ASM filetmp2.fonserver2.
Example 28-3 Navigating Oracle ASM Folders
ftp> open myhost 7777
ftp> user system
Password required for SYSTEM
Password: password
ftp> cd /sys/asm
ftp> ls
DATA
RECOVERY
ftp> cd DATA
ftp> ls
dbs
MFG
ftp> cd dbs
ftp> ls
t_dbl.f
t_axl.f
ftp> binary
ftp> get t_dbl.f, t_axl.f
ftp> put my_db2.f
Example 28-4 Transferring Oracle ASM Files Between Databases with FTP proxy Method
1 ftp> open server1 port1 2 ftp> user username1 3 Password required for USERNAME1 4 Password: password-for-username1 5 ftp> cd /sys/asm/DATAFILE/MFG/DATAFILE 6 ftp> proxy open server2 port2 7 ftp> proxy user username2 8 Password required for USERNAME2 9 Password: password-for-username2 10 ftp> proxy cd /sys/asm/DATAFILE/MFG/DATAFILE 11 ftp> proxy put dbs2.f tmp1.f 12 ftp> proxy get dbs1.f tmp2.f
28.3.1.6 Using FTP on the Standard Port Instead of the Oracle XML DB Default Port
You can use the Oracle XML DB configuration file, xdbconfig.xml, to configure FTP to listen on any port. By default, FTP listens on a non-standard, unprotected port.
To use FTP on the standard port, 21, your database administrator must do the following:
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Net Services Reference for information about listener parameters and file
listener.ora -
Oracle Database Net Services Reference, section "Port Number Limitations" for information about running on privileged ports
28.3.1.7 Using IPv6 IP Addresses with FTP
Starting with 11g Release 2 (11.2), Oracle Database supports the use of Internet Protocol Version 6, IPv6 (in addition to Internet Protocol Version 4).
Example 28-5 shows how to make an FTP connection with the IPv6 address 2001::0db8:ffff:ffff:ffff.
See Also:
Oracle Database Net Services Reference for information about IPv6
Example 28-5 FTP Connection Using IPv6
ftp> open 2001::0db8:ffff:ffff:ffff 1521 Connected to 2001::0db8:ffff:ffff:ffff. 220- xmlhost.example.com Unauthorized use of this FTP server is prohibited and may be subject to civil and criminal prosecution. 220- xmlhost.example.com FTP server (Oracle XML DB/Oracle Database) ready. User (2001::0db8:ffff:ffff:ffff:(none)): username 331 pass required for USERNAME Password: password-for-username 230 USERNAME logged in ftp>
28.3.1.8 FTP Server Session Management
Oracle XML DB protocol server provides session management for FTP. After a short wait for a new command, FTP returns to the protocol layer and the shared server is freed up to serve other connections.
The duration of this short wait is configurable by changing parameter call-timeout in the Oracle XML DB configuration file. For high traffic sites, call-timeout should be shorter, so that more connections can be served. When new data arrives on the connection, the FTP server is re-invoked with fresh data. So, the long running nature of FTP does not affect the number of connections which can be made to the protocol server.
See Also:
Configuration of Oracle XML DB Using xdbconfig.xml for information about configuring Oracle XML DB parameters
28.3.1.9 Handling Error 421. Modifying the Default Timeout Value of an FTP Session
If you are frequently disconnected from the server and you must reconnect and traverse the entire directory before performing the next operation, then you might need to modify the default timeout value for FTP sessions. If the session is idle for more than this period, it is disconnected.
You can increase the timeout value (default = 6000 centiseconds) by modifying the configuration document as follows and then restarting the database:
Example 28-6 Modifying the Default Timeout Value of an FTP Session
DECLARE
newconfig XMLType;
BEGIN
SELECT XMLQuery('copy $i := $p1 modify
(for $j in $i/xdbconfig/sysconfig/protocolconfig/ftpconfig/session-timeout
return replace value of node $j with $p2)
return $i'
PASSING DBMS_XDB_CONFIG.cfg_get() AS "p1", 123456789 AS "p2" RETURNING CONTENT)
INTO newconfig FROM DUAL;
DBMS_XDB_CONFIG.cfg_update(newconfig);
END;/
COMMIT;
28.3.1.10 FTP Client Failure in Passive Mode
Do not use FTP in passive mode to connect remotely to a server that has HOSTNAME configured in listener.ora as localhost or 127.0.0.1.
If the HOSTNAME specified in server file listener.ora is localhost or 127.0.0.1, then the server is configured for local use only. If you try to connect remotely to the server using FTP in passive mode, the FTP client fails. This is because the server passes IP address 127.0.0.1 (derived from HOSTNAME) to the client, which makes the client try to connect to itself, not to the server.
28.4 HTTP(S) and Oracle XML DB Protocol Server
Oracle XML DB implements HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP), HTTP 1.1 as defined in the RFC2616 specification.
28.4.1 Oracle XML DB Protocol Server: HTTP(S) Features
The Oracle XML DB HTTP(S) component of the Oracle XML DB protocol server implements the RFC2616 specification with the exception of a few optional features.
These are the optional HTTP(S) features that are not supported:
-
gzipand compress transfer encodings -
byte-range headers
-
The
TRACEmethod (used for proxy error debugging) -
Cache-control directives (these require you to specify expiration dates for content, and are not generally used)
-
TE, Trailer, Vary & Warning headers
-
Weak entity tags
-
Web common log format
-
Multi-homed Web server
See Also:
RFC 2616, HTTP 1.1 Protocol Specification, http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616.txt
28.4.1.1 Supported HTTP(S) Client Methods
Oracle XML DB supports several HTTP(S) client methods for access to Oracle XML DB Repository.
-
OPTIONS– get information about available communication options -
GET– get document/data (including headers) -
HEAD– get headers only, without document body -
PUT– store data in resource -
DELETE– delete resource
The semantics of these HTTP(S) methods are in accordance with WebDAV. Servlets and Web services may support additional HTTP(S) methods, such as POST.
See Also:
WebDAV Client Methods Supported by Oracle XML DB for supported HTTP(S) client methods involving WebDAV
28.4.1.2 Using HTTP(S) on a Standard Port Instead of an Oracle XML DB Default Port
You can use the Oracle XML DB configuration file, xdbconfig.xml, to configure HTTP(S) to listen on any port. By default, HTTP(S) listens on a non-standard, unprotected port.
To use HTTP or HTTPS on a standard port (80 for HTTP, 443 for HTTPS), your database administrator must do the following:
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Net Services Reference for information about listener parameters and file
listener.ora -
Oracle Database Net Services Reference, section "Port Number Limitations" for information about running on privileged ports
28.4.1.3 Use of IPv6 IP Addresses with HTTP(S)
Starting with 11g Release 2 (11.2), Oracle Database supports the use of Internet Protocol Version 6, IPv6 (in addition to Internet Protocol Version 4). IPv6 addresses in URLs are enclosed in brackets ([]).
Here is an example:
http://[2001::0db8:ffff:ffff:ffff]:8080/
See Also:
Oracle Database Net Services Administrator's Guide for information about IPv6
28.4.1.4 HTTPS: Support for Secure HTTP
If properly configured, you can access Oracle XML DB Repository in a secure fashion, using HTTPS.
See Configuring Secure HTTP (HTTPS) for configuration information.
Note:
If Oracle Database is installed on Microsoft Windows XP with Service Pack 2 (SP2), then you must use HTTPS for WebDAV access to Oracle XML DB Repository, or else you must make appropriate modifications to the Windows XP Registry. For information about the latter, see http://www.microsoft.com/technet/prodtechnol/winxppro/maintain/sp2netwk.mspx#XSLTsection129121120120
28.4.1.5 Control of URL Expiration Time
Optional configuration parameter expire specifies an HTTP Expires header. This header acts as a directive to the HTTP client, to specify the expiration date and time for a URL.
If cached, the document targeted by a URL can be fetched from the client cache rather than from the server, until this expiration time has passed. After that time, the cache copy is out-of-date and a new copy must be obtained from the source (server).
The Oracle XML DB syntax for the Expires header, which is used in the expire configuration element, is a subset of the so-called alternate syntax defined for the ExpiresDefault directive of the Apache module mod_expires. See http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.0/mod/mod_expires.html#AltSyn for that syntax.
These are the Oracle XML DB restrictions to the ExpiresDefault syntax:
-
You cannot use
accessas the<base>. Onlynowandmodificationare allowed. -
The
<type>values must appear in order of decreasing time period. For example,yearmust appear before, not after,month, since a year is a longer time period than a month. -
You can use at most one occurrence of each of the different
<type>values. For example, you cannot have multipleyearentries or multipledayentries.
28.4.1.6 Anonymous Access to Oracle XML DB Repository Using HTTP
Optional configuration parameter allow-repository-anonymous-access controls whether or not anonymous HTTP access to Oracle XML DB Repository data is allowed using an unlocked ANONYMOUS user account. The default value is false, meaning that unauthenticated access to repository data is blocked.
To allow anonymous HTTP access to the repository, you must set this parameter to true, and unlock the ANONYMOUS user account.
Caution:
There is an inherent security risk associated with allowing anonymous access to the repository.
Parameter allow-repository-anonymous-access does not control anonymous access to the repository using servlets. Each servlet has its own security-role-ref parameter value to control its access.
Note:
If user account ANONYMOUS is locked for a multitenant container database (CDB) then locking or unlocking ANONYMOUS for a pluggable database (PDB) plugged into that CDB has no effect on access by ANONYMOUS to the PDB.
See Also:
-
Table 28-3 for information about parameter
allow-repository-anonymous-access -
Configuration of Oracle XML DB Using xdbconfig.xml for information about configuring Oracle XML DB parameters
-
Configuration of Oracle XML DB Servlets for information about parameter
security-role-ref
28.4.1.7 Use of Java Servlets with HTTP(S)
Oracle XML DB supports the use of Java servlets. Each must each be registered with a unique name in the Oracle XML DB configuration file, along with parameters to customize its action. It should be compiled and loaded into the database. The servlet name must be associated with a pattern.
The pattern can be an extension such as *.jsp or a path name such as /a/b/c or /sys/*, as described in Java servlet application program interface (API) version 2.2.
While processing an HTTP(S) request, the path name for the request is matched against the registered patterns. If there is a match then the protocol server invokes the corresponding servlet with the appropriate initialization parameters. The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is started, and it invokes a Java method to initialize the servlet, create response and request objects, pass these on to the servlet, and run the servlet.
28.4.1.8 Embedded PL/SQL Gateway
You can use the embedded PL/SQL gateway to implement a Web application entirely in PL/SQL. It runs in the Oracle XML DB HTTP listener.
With the embedded PL/SQL gateway, a Web browser sends an HTTP(S) request in the form of a URL that identifies a stored procedure and provides it with parameter values. The gateway translates the URL, calls the stored procedure with the parameter values, and returns output (typically HTML) to the Web-browser client.
Using the embedded PL/SQL gateway simplifies installation, configuration, and administration of PL/SQL based Web applications. The embedded gateway uses the Oracle XML DB protocol server, not Oracle HTTP Server. Its configuration is defined by the Oracle XML DB configuration file, xdbconfig.xml. However, the recommended way to configure the embedded gateway is to use the procedures in PL/SQL package DBMS_EPG, not to edit file xdbconfig.xml.
Note:
If you are currently using mod_plsql, which is a plug-in of Oracle HTTP Server that lets you invoke PL/SQL stored procedures using HTTP(S), Oracle recommends that you migrate to using the embedded PL/SQL gateway instead.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Development Guide for information about configuring and using the embedded PL/SQL gateway
-
Administration of Oracle XML DB for information on the configuration definition of the embedded gateway in
xdbconfig.xml
28.4.1.9 Transmission of Multibyte Data From a Client
When a client sends multibyte data in a URL, RFC 2718 specifies that the client should use the %HH format, where HH is the hexadecimal notation of the byte value in UTF-8 encoding.
The following are URL examples that can be sent to Oracle XML DB in an HTTP(S) or WebDAV context:
http://urltest/xyz%E3%81%82%E3%82%A2 http://%E3%81%82%E3%82%A2 http://%E3%81%82%E3%82%A2/abc%E3%81%86%E3%83%8F.xml
Oracle XML DB processes the requested URL, any URLs within an IF header, any URLs within the DESTINATION header, and any URLs in the REFERRED header that contains multibyte data.
The default-url-charset configuration parameter can be used to accept requests from some clients that use other, nonconforming, forms of URL, with characters that are not ASCII. If a request with such characters fails, try setting this value to the native character set of the client environment. The character set used in such URL fields must be specified with an IANA charset name.
default-url-charset controls the encoding for nonconforming URLs. It is not required to be set unless a nonconforming client that does not send the Content-Type charset is used.
See Also:
-
RFC 2616, HTTP 1.1 Protocol Specification,
http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616.txt -
Configuration of Oracle XML DB Using xdbconfig.xml for information about configuring Oracle XML DB parameters
28.4.1.10 Characters That Are Not ASCII in URLs
Convert non-ASCII characters that appear in URLs passed to an HTTP server to UTF-8 and escape them using the %HH format, where HH is the hexadecimal notation of the byte value.
For flexibility, the Oracle XML DB protocol server interprets the incoming URLs by testing whether it is encoded in one of the following character sets, in the order presented here:
-
UTF-8
-
Charset parameter of the
Content-Typefield of the request, if specified -
Character set, if specified, in the
default-url-charsetconfiguration parameter -
Character set of the database
See Also:
Configuration of Oracle XML DB Using xdbconfig.xml for information about configuring Oracle XML DB parameters
28.4.1.11 Character Sets for HTTP(S)
You can control the character sets used for data that is transferred using HTTP(S).
28.4.1.11.1 HTTP(S) Request Character Set
The character set of an HTTP(S) request body is determined using a straightforward but somewhat complex algorithm.
-
The Content-Type header is evaluated. If the Content-Type header specifies a charset value, the specified charset is used.
-
The MIME type of the document is evaluated as follows:
-
If the MIME type is "
*/xml" then the character set is determined as follows:-
If neither a BOM nor an encoding declaration is present then
UTF-8is used. -
If a BOM is present then
UTF-16is used. -
If an encoding declaration is present then the specified encoding is used.
-
-
If the MIME type is
textthenISO8859-1is used. -
If the MIME type is neither "
*/xml" nortextthen the database character set is used.
-
There is a difference between HTTP(S) and SQL or FTP. For text documents, the default is ISO8859-1, as specified by the IETF.org RFC 2616: HTTP 1.1 Protocol Specification.
28.4.1.11.2 HTTP(S) Response Character Set
The response generated by the Oracle XML DB HTTP server is in a character set specified in the Accept-Charset field of the request.
Accept-Charset can specify a list of character sets. Based on the q-value, Oracle XML DB chooses one of them that does not require conversion. This might not necessarily be the character set with the highest q-value. If Oracle XML DB cannot find one that does not require conversion, then the conversion used is based on the highest q-value.
28.5 WebDAV and Oracle XML DB
Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV) is an IETF standard protocol that Oracle XML DB uses to provide users with a file-system interface to Oracle XML Repository over the Internet. The most popular way of accessing a WebDAV server folder is through WebFolders using Microsoft Windows.
WebDAV is an extension to the HTTP 1.1 protocol that lets an HTTP server act as a file server. It lets clients perform remote Web content authoring through a coherent set of methods, headers, request body formats and response body formats. For example, a DAV-enabled editor can interact with an HTTP/WebDAV server as if it were a file system. WebDAV provides operations to store and retrieve resources, create and list contents of resource collections, lock resources for concurrent access in a coordinated manner, and to set and retrieve resource properties.
28.5.1 Oracle XML DB WebDAV Features
Oracle XML DB supports the foldering and access-control features of WebDAV. Foldering is specified by RFC2518.
WebDAV is a set of extensions to the HTTP(S) protocol that allow you to share, edit, and manage your files on remote Web servers.
See Also:
RFC 2518: WebDAV Protocol Specification, http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2518.txt
28.5.1.1 WebDAV Features That Are Not Supported by Oracle XML DB
Oracle XML DB supports specification RFC2518, with the exception of a few features. For methods COPY, MOVE and DELETE it also supports the binding of resources as described in specification RFC5842.
These are the WebDAV features from RFC2518 that Oracle XML DB does not support:
-
Using the name of a write-locked null resource (a lock-null resource) as a folder name is not supported, because it is represented as a zero-length resource in the file system. This is an optional feature.
-
For method
LOCK, you cannot specify infinity for the depth, to simultaneously lock a resource and all of its descendents. This feature is not optional, but it is not supported by Oracle XML DB.
In addition, for methods COPY, MOVE and DELETE Oracle XML DB supports the binding of resources as described in section 2 of RFC5842, “Binding Extensions to Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV)”. A binding is a mapping of a URI to a resource, for a given folder.
See Also:
-
Section 7.4 of the RFC2518 specification,
http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc2518.html#rfc.section.7.4for information about lock-null resources -
Section 9.2 of the RFC2518 specification,
http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc2518.html#rfc.section.9.2for information about depth-infinity locks -
Section 2 of the RFC5842 specification,
https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5842#section-2for information about resource bindings
28.5.1.2 WebDAV Client Methods Supported by Oracle XML DB
Oracle XML DB supports several HTTP(S)/WebDAV client methods for access to Oracle XML DB Repository.
-
PROPFIND(WebDAV-specific) – get properties for a resource -
PROPPATCH(WebDAV-specific) – set or remove resource properties -
LOCK(WebDAV-specific) – lock a resource (create or refresh a lock) -
UNLOCK(WebDAV-specific) – unlock a resource (remove a lock) -
COPY(WebDAV-specific) – copy a resource -
MOVE(WebDAV-specific) – move a resource -
MKCOL(WebDAV-specific) – create a folder resource (collection)
See Also:
-
Supported HTTP(S) Client Methods for additional supported HTTP(S) client methods
-
Privileges for information about WebDAV privileges
28.5.2 WebDAV and Microsoft Windows XP SP2
For Microsoft Windows XP with Service Pack 2 (SP2), you must use a secure connection (HTTPS) for WebDAV access to Oracle XML DB Repository, or else you must make appropriate modifications to the Windows XP Registry.
See Also:
-
http://www.microsoft.com/technet/prodtechnol/winxppro/maintain/sp2netwk.mspx#XSLTsection129121120120for information about making necessary modifications to the Windows XP registry
28.5.3 Creating a WebFolder in Microsoft Windows For Use With Oracle XML DB Repository
Create a WebFolder in Windows 2000 and use it with Oracle XML DB Repository.
Create a WebFolder in Windows 2000:
You can access Oracle XML DB Repository the same way you access any Windows folder.
Figure 28-2 Creating a WebFolder in Microsoft Windows
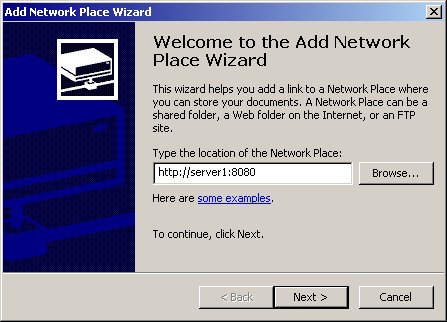
Description of "Figure 28-2 Creating a WebFolder in Microsoft Windows"
28.5.3.1 Use of WebDAV with Windows Explorer to Copy Files into Oracle XML DB Repository
You can use Windows Explorer to insert a folder from a local hard drive into Oracle Database.
Figure 28-3 illustrates this.
Windows Explorer includes support for the WebDAV protocol. WebDAV extends the HTTP standard, adding additional verbs that allow an HTTP server to act as a file server.
When a Windows Explorer copy operation or FTP input command is used to transfer a number of documents into Oracle XML DB Repository, each put or post command is treated as a separate atomic operation. This ensures that the client does not get confused if one of the file transfers fails. It also means that changes made to a document through a protocol are visible to other users as soon as the request has been processed.
Figure 28-3 Copying Files into Oracle XML DB Repository
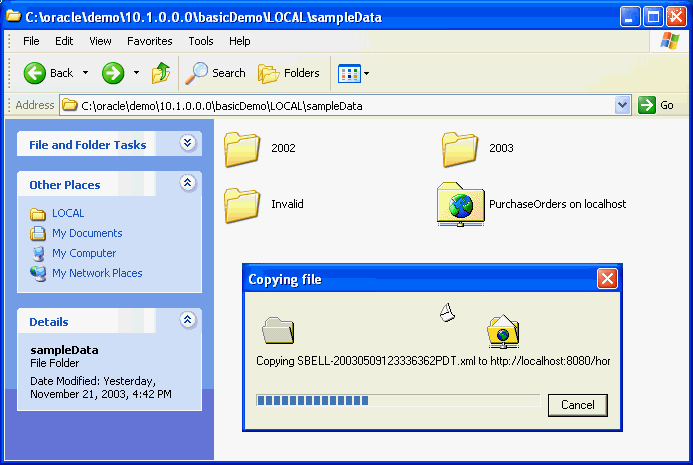
Description of "Figure 28-3 Copying Files into Oracle XML DB Repository"
Footnote Legend
Footnote 1:BOM is a Unicode-standard signature that indicates the order of the stream of bytes that follows it.