Managing Performance Policies
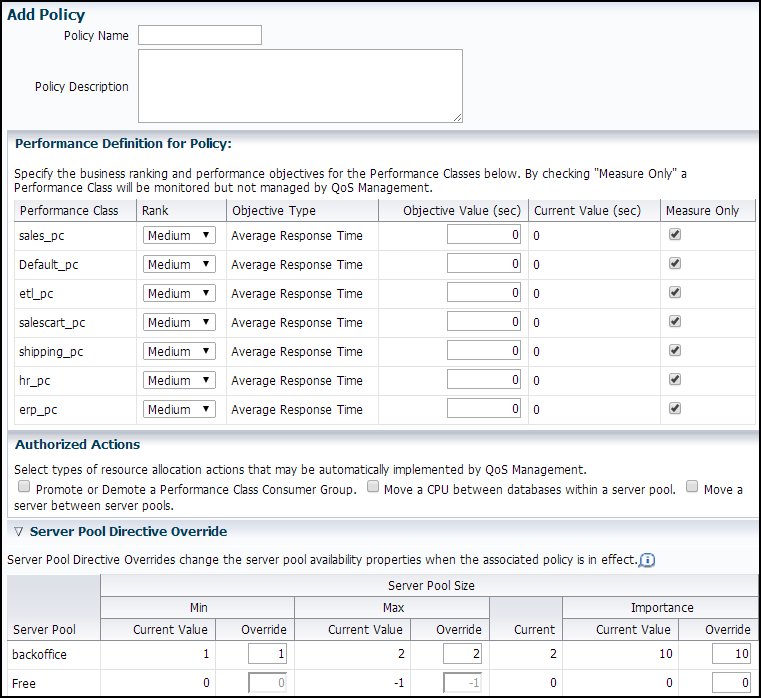
Creating a Performance Policy and Specifying Performance Objectives
Use Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control to create a Performance Policy.
To create and configure a Performance Policy, perform the following steps:
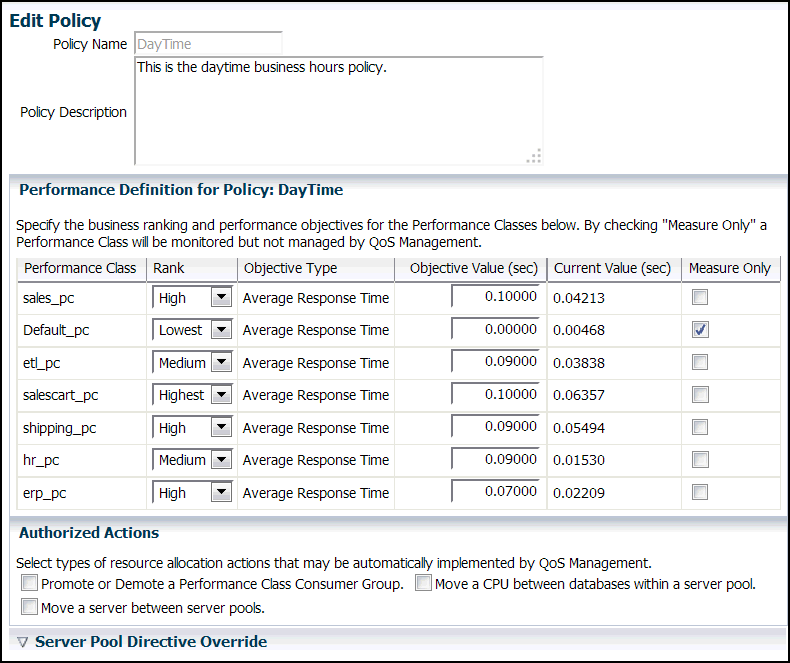
Editing an Existing Performance Policy
On the Edit Policy page, you can change the rank of each Performance Class, or change the Measure Only setting for a Performance Class. You can also select the type of resource allocation actions that can be automatically implemented by QoS Management and set server pool directive overrides.
See Also:
-
"Monitoring Performance with Oracle Database QoS Management"
-
"Setting Server Pool Directive Overrides" for more information on server pool directive overrides
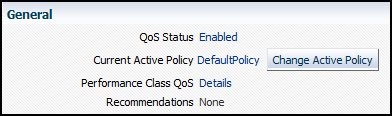
Setting the Current Performance Policy
A Performance Policy is a collection of Performance Objectives, one for each Performance Class, that are in force at the same time. There are multiple ways to modify the active Performance Policy for Oracle Database QoS Management.
Changing the Active Performance Policy from the Policy Set Editor Wizard
You can change the Performance Policy that will be active when you submit the Policy Set to Oracle Database QoS Management.
- Start the Policy Set Editor wizard.
- Proceed to the fifth page in the wizard, which is titled Edit Policy Set: Set Policy.
- Select the Performance Policy you want enforced, and click Set Policy.
At the end of the Policy Set Editor wizard, you can review the settings you specified, then click Submit Policy Set to configure Oracle Database QoS Management.
Changing the Active Performance Policy using a Script
Many Oracle Database QoS Management policies are calendar based. You can switch the active performance policy automatically through a job scheduler such as Enterprise Manager Cloud Control, Task Scheduler or CRON by using a QOSCTL command to set the active policy.
Related Topics
Deleting a Performance Policy
- Start the Policy Set Editor wizard.
- Proceed to the fourth page in the wizard, which is titled Edit Policy Set: Performance Policies.
- Click the Delete Policy button to delete a Performance Policy.
- You then advance to the end of the Edit Policy Set wizard, and click Submit Policy Set to make the change permanent.
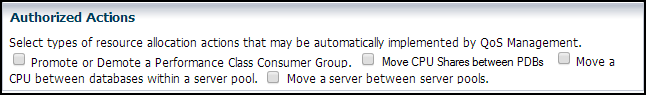
Automatically Implementing Recommendations for a Performance Policy
You can use the appropriate check boxes to specify which of the following actions can be implemented automatically by Oracle Database QoS Management:
-
Promote or demote a performance class consumer group
-
Move a CPU between databases within a server pool
-
Move CPU shares between PDBs
-
Move a server between server pools
If you do not authorize any of these actions, then Oracle Database QoS Management does not implement any changes to the active system until you review the current Recommendations for a Performance Class and click the Implement button.
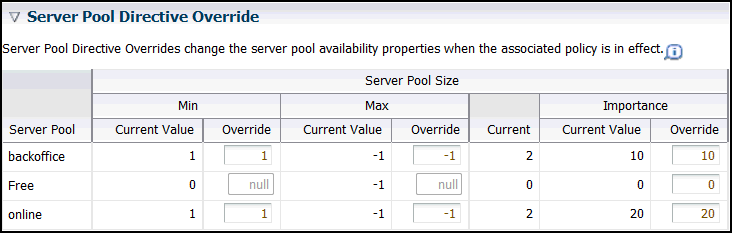
Setting Server Pool Directive Overrides
A server pool directive override gives you the ability to enforce different settings for server pool sizes, or change the importance of server pools. For example, if you are expecting a surge in demand, such as during an advertised sale period, then you could use a server pool directive override to allocate more resources to the accounting applications.
webapps, HR, and payroll. You create a server pool directive override to increase the minimum server pool size for the payroll server pool. When the server pool directive override is active, a server could be removed from the HR or webapps server pool to satisfy the higher minimum server requirement of the payroll server pool.
See Also:
"Modifying Server Pool Settings" for more information about configuring the server pool settings