12 Integrating Oracle Database Vault with Other Oracle Products
You can integrate Oracle Database Vault with other Oracle products, such as Oracle Enterprise User Security.
- Integrating Oracle Database Vault with Enterprise User Security
You can integrate Oracle Database Vault with Oracle Enterprise User Security. - Configuring Oracle Database Vault Accounts as Enterprise User Accounts
You can configure existing Oracle Database Vault user accounts as enterprise user accounts. - Integration of Oracle Database Vault with Transparent Data Encryption
Transparent Data Encryption complements Oracle Database Vault in that it provides data protection when the data leaves the secure perimeter of the database. - Attaching Factors to an Oracle Virtual Private Database
You can attach factors to an Oracle Virtual Private Database. - Integrating Oracle Database Vault with Oracle Label Security
You can integrate Oracle Database Vault with Oracle Label Security, and check the integration with reports and data dictionary views. - Integrating Oracle Database Vault with Oracle Data Guard
An Oracle Database Vault-Oracle Data Guard integration requires first, the primary database configuration, then the standby database configration. - Registering Oracle Internet Directory Using Oracle Database Configuration Asssitant
You can use Oracle Internet Directory in an Oracle Database Vault-enabled database.
Integrating Oracle Database Vault with Enterprise User Security
You can integrate Oracle Database Vault with Oracle Enterprise User Security.
- About Integrating Oracle Database Vault with Enterprise User Security
Enterprise User Security centrally manages database users and authorizations in one place. - Configuring an Enterprise User Authorization
To configure an Enterprise User authorization, you must create an Oracle Database Vault rule set to control the user access.
About Integrating Oracle Database Vault with Enterprise User Security
Enterprise User Security centrally manages database users and authorizations in one place.
It is combined with Oracle Identity Management and is available in Oracle Database Enterprise Edition.
In general, to integrate Oracle Database Vault with Oracle Enterprise User Security, you configure the appropriate realms to protect the data that you want to protect in the database.
After you define the Oracle Database Vault realms as needed, you can create a rule set for the Enterprise users to allow or disallow their access.
See Also:
Oracle Database Enterprise User Security Administrator's Guide for more information about Enterprise User Security
Configuring Oracle Database Vault Accounts as Enterprise User Accounts
You can configure existing Oracle Database Vault user accounts as enterprise user accounts.
See Also:
Oracle Database Enterprise User Security Administrator's Guide for detailed information about the User Migration Utility
Integration of Oracle Database Vault with Transparent Data Encryption
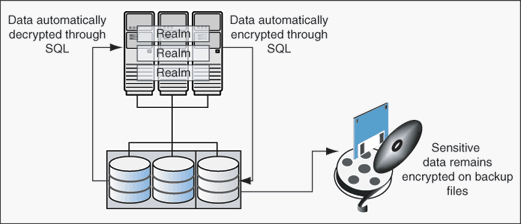
Transparent Data Encryption complements Oracle Database Vault in that it provides data protection when the data leaves the secure perimeter of the database.
With Transparent Data Encryption, a database administrator or database security administrator can simply encrypt columns with sensitive content in application tables, or encrypt entire application tablespaces, without any modification to the application.
If a user passes the authentication and authorization checks, Transparent Data Encryption automatically encrypts and decrypts information for the user. This way, you can implement encryption without having to change your applications.
Once you have granted the Transparent Data Encryption user the appropriate privileges, then Transparent Data Encryption can be managed as usual and be used complimentary to Database Vault.
Figure 12-1 shows how Oracle Database Vault realms handle encrypted data.
Figure 12-1 Encrypted Data and Oracle Database Vault
Description of "Figure 12-1 Encrypted Data and Oracle Database Vault"
See Also:
Oracle Database Advanced Security Guide for detailed information about Transparent Data EncryptionAttaching Factors to an Oracle Virtual Private Database
You can attach factors to an Oracle Virtual Private Database.
- Define a Virtual Private Database policy predicate that is a PL/SQL function or expression.
- For each function or expression, use the
DVF.F$PL/SQL function that is created for each factor.
See Also:
Oracle Database Security Guide Oracle Database Security Guide for more information about Oracle Virtual Private Database
Integrating Oracle Database Vault with Oracle Label Security
You can integrate Oracle Database Vault with Oracle Label Security, and check the integration with reports and data dictionary views.
- How Oracle Database Vault Is Integrated with Oracle Label Security
An Oracle Database Vault-Oracle Label Security integration enables you to assign an OLS label to a Database Vault factor identity. - Requirements for Using Oracle Database Vault with Oracle Label Security
You must fulfill specific requirements in place before you use Oracle Database Vault with Oracle Label Security. - Using Oracle Database Vault Factors with Oracle Label Security Policies
To enhance security, you can integrate Oracle Database Vault factors with Oracle Label Security policies. - Tutorial: Integrating Oracle Database Vault with Oracle Label Security
An Oracle Database Vault-Oracle Label Security integration can grant different levels of access to two administrative users who have the same privileges. - Related Reports and Data Dictionary Views
Oracle Database Vault provides reports and data dictionary views that list information about the Oracle Database Vault-Oracle Label Security integration.
How Oracle Database Vault Is Integrated with Oracle Label Security
An Oracle Database Vault-Oracle Label Security integration enables you to assign an OLS label to a Database Vault factor identity.
In Oracle Label Security, you can restrict access to records in database tables or PL/SQL programs. For example, Mary may be able to see data protected by the HIGHLY SENSITIVE label, an Oracle Label Security label on the EMPLOYEE table that includes records that should have access limited to certain managers. Another label can be PUBLIC, which allows more open access to this data.
In Oracle Database Vault, you can create a factor called Network, for the network on which the database session originates, with the following identities:
-
Intranet: Used for when an employee is working on site within the intranet for your company.
-
Remote: Used for when the employee is working at home from a VPN connection.
You then assign a maximum session label to both. For example:
-
Assign the Intranet identity to the HIGHLY SENSITIVE Oracle Label Security label.
-
Assign the Remote identity to the PUBLIC label.
This means that when Mary is working at home using her VPN connection, she has access only to the limited table data protected under the PUBLIC identity. But when she is in the office, she has access to the HIGHLY SENSITIVE data, because she is using the Intranet identity. Tutorial: Integrating Oracle Database Vault with Oracle Label Security provides an example of how to accomplish this type of integration.
In a non-unified auditing environment, you can audit the integration with Oracle Label Security by using the Label Security Integration Audit Report. Oracle Database Vault writes the audit trail to the DVSYS.AUDIT_TRAIL$ table. If unified auditing is enabled, then you can create audit policies to capture this information, as described in Oracle Database Security Guide.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Vault Oracle Label Security APIs for information about Database Vault APIs that you can use to integrate Database Vault with Oracle Label Security
-
Related Reports and Data Dictionary Views for information about reports that you can run on the Oracle Database Vault and Oracle Label Security integration
-
Oracle Label Security Administrator’s Guide for more information about Oracle Label Security labels
Requirements for Using Oracle Database Vault with Oracle Label Security
You must fulfill specific requirements in place before you use Oracle Database Vault with Oracle Label Security.
-
Oracle Label Security is licensed separately. Ensure that you have purchased a license to use it.
-
Before you install Oracle Database Vault, you must have already installed Oracle Label Security.
-
The installation process for Oracle Label Security creates the
LBACSYSuser account. As a user who has been granted theDV_ACCTMGRrole, unlock this account and grant it a new password. For example:sqlplus bea_dvacctmgr -- Or, sqlplus bea_dvacctmgr@hrpdb for a PDB Enter password: password ALTER USER LBACSYS ACCOUNT UNLOCK IDENTIFIED BY password;
Follow the guidelines in Oracle Database Security Guide to replace
passwordwith a password that is secure. -
If you plan to use the
LBACSYSuser account in Oracle Enterprise Manager, then log into Enterprise Manager as userSYSwith theSYSDBAadministrative privilege, and grant this user theSELECT ANY DICTIONARYandSELECT_CATALOG_ROLEsystem privileges. -
Ensure that you have the appropriate Oracle Label Security policies defined. For more information, see Oracle Label Security Administrator’s Guide.
-
If you plan to integrate an Oracle Label Security policy with a Database Vault policy, then ensure that the policy name for Oracle Label Security is less than 24 characters. You can check the names of Oracle Label Security policies by querying the
POLICY_NAMEcolumn of theALL_SA_POLICIESdata dictionary view.
Using Oracle Database Vault Factors with Oracle Label Security Policies
To enhance security, you can integrate Oracle Database Vault factors with Oracle Label Security policies.
- About Using Oracle Database Vault Factors with Oracle Label Security Policies
And Oracle Database Vault-Oracle Label Security integration enables you to control the maximum security clearance for a database session. - Configuring Factors to Work with an Oracle Label Security Policy
You can define factors that contribute to the maximum allowable data label of an Oracle Label Security policy.
About Using Oracle Database Vault Factors with Oracle Label Security Policies
And Oracle Database Vault-Oracle Label Security integration enables you to control the maximum security clearance for a database session.
Oracle Database Vault controls the maximum security clearance for a database session by merging the maximum allowable data for each label in a database session by merging the labels of Oracle Database Vault factors that are associated to an Oracle Label Security policy.
In brief, a label acts as an identifier for the access privileges of a database table row. A policy is a name associated with the labels, rules, and authorizations that govern access to table rows.
See Also:
Oracle Label Security Administrator’s Guide for more information about row labels and policiesConfiguring Factors to Work with an Oracle Label Security Policy
You can define factors that contribute to the maximum allowable data label of an Oracle Label Security policy.
Note:
If you do not associate an Oracle Label Security policy with factors, then Oracle Database Vault maintains the default Oracle Label Security behavior for the policy.
Tutorial: Integrating Oracle Database Vault with Oracle Label Security
An Oracle Database Vault-Oracle Label Security integration can grant different levels of access to two administrative users who have the same privileges.
- About This Tutorial
You can use Oracle Database Vault factors with Oracle Label Security and Oracle Virtual Private Database (VPD) to restrict sensitive data access. - Step 1: Create Users for This Tutorial
You must create two administrative users for this tutorial. - Step 2: Create the Oracle Label Security Policy
Next, you can create the Oracle Label Security policy and grant users the appropriate privileges for it. - Step 3: Create Oracle Database Vault Rules to Control the OLS Authorization
After you create the Oracle Label Security policy, you can create Database Vault rules to work with it. - Step 4: Update the ALTER SYSTEM Command Rule to Use the Rule Set
Before the rule set can be used, you must update the ALTER SYSTEM command rule, which is a default command rule. - Step 5: Test the Authorizations
With all the components in place, you are ready to test the authorization. - Step 6: Remove the Components for This Tutorial
You can remove the components that you created for this tutorial if you no longer need them.
About This Tutorial
You can use Oracle Database Vault factors with Oracle Label Security and Oracle Virtual Private Database (VPD) to restrict sensitive data access.
You can restrict this data so that it is only exposed to a database session when the correct combination of factors exists, defined by the security administrator, for any given database session.
Step 2: Create the Oracle Label Security Policy
Next, you can create the Oracle Label Security policy and grant users the appropriate privileges for it.
Step 3: Create Oracle Database Vault Rules to Control the OLS Authorization
After you create the Oracle Label Security policy, you can create Database Vault rules to work with it.
Step 4: Update the ALTER SYSTEM Command Rule to Use the Rule Set
Before the rule set can be used, you must update the ALTER SYSTEM command rule, which is a default command rule.
Step 5: Test the Authorizations
With all the components in place, you are ready to test the authorization.
Related Reports and Data Dictionary Views
Oracle Database Vault provides reports and data dictionary views that list information about the Oracle Database Vault-Oracle Label Security integration.
Table 12-1 lists the Oracle Database Vault reports. See Oracle Database Vault Reports , for information about how to run these reports.
Table 12-1 Reports Related to Database Vault and Oracle Label Security Integration
| Report | Description |
|---|---|
|
Lists factors in which the Oracle Label Security policy does not exist. |
|
|
Lists invalid label identities (the Oracle Label Security label for this identity has been removed and no longer exists). |
|
|
Lists accounts and roles that have the |
Table 12-2 lists data dictionary views that provide information about existing Oracle Label Security policies used with Oracle Database Vault.
Table 12-2 Data Dictionary Views Used for Oracle Label Security
| Data Dictionary View | Description |
|---|---|
|
Lists the Oracle Label Security policies defined |
|
|
Lists the factors that are associated with Oracle Label Security policies |
|
|
Lists the Oracle Label Security label for each factor identifier in the |
Integrating Oracle Database Vault with Oracle Data Guard
An Oracle Database Vault-Oracle Data Guard integration requires first, the primary database configuration, then the standby database configration.
- Step 1: Configure the Primary Database
You must run the DGMGRL and DBCA utilities, and then theALTER SYSTEMstatement, to configure the primary database. - Step 2: Configure the Standby Database
You can perform the standby database configuration within the database to be used for the standby database.
Step 1: Configure the Primary Database
You must run the DGMGRL and DBCA utilities, and then the ALTER SYSTEM statement, to configure the primary database.
-
For Linux and UNIX systems, ensure there is an
/etc/oratabentry for the database on the node in which you are installing Oracle Database Vault. -
If you are using Data Guard Broker, then from the command prompt, disable the configuration as follows:
dgmgrl sys Enter password: password DGMGRL> disable configuration; -
Run Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA) and configure the database options to add Oracle Database Vault to the primary database.
-
From the command line, enter the following command to start DBCA:
dbca
-
Select the correct database type (Cluster or Single Instance) and click Next.
-
In the Database Operation page, select Configure Database Options and click Next.
-
Select the appropriate database and click Next.
-
Select Oracle Label Security, which then enables you to select Oracle Database Vault and click Next.
-
Enter the name of the Database Vault owner (required) and the Database Vault account manager (recommended).
Passwords must have at least one alphabetic character, one number, and one special character.
-
Click Next.
-
Choose appropriate connection mode and click Next.
-
Click OK to restart the database.
-
Click OK on Configure Additional Components.
At this point, the installation on the primary site is complete.
-
-
Log into the database instance as user
SYSwith theSYSDBAadministrative privilege.sqlplus sys as sysdba Enter password: password -
Run the following
ALTER SYSTEMstatements:ALTER SYSTEM SET AUDIT_SYS_OPERATIONS=TRUE SCOPE=SPFILE; ALTER SYSTEM SET OS_ROLES=FALSE SCOPE=SPFILE; ALTER SYSTEM SET RECYCLEBIN='OFF' SCOPE=SPFILE; ALTER SYSTEM SET REMOTE_LOGIN_PASSWORDFILE='EXCLUSIVE' SCOPE=SPFILE; ALTER SYSTEM SET SQL92_SECURITY=TRUE SCOPE=SPFILE; ALTER SYSTEM SET REMOTE_OS_AUTHENT=FALSE SCOPE=SPFILE; ALTER SYSTEM SET REMOTE_OS_ROLES=FALSE SCOPE=SPFILE;
-
Run the
ALTER SYSTEMstatement on each database instance to set the parameters as shown in Step 5. -
Restart each database instance.
CONNECT SYS AS SYSOPER Enter password: password SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE STARTUP
Registering Oracle Internet Directory Using Oracle Database Configuration Asssitant
You can use Oracle Internet Directory in an Oracle Database Vault-enabled database.
However, if you want to register Oracle Internet Directory (OID) using Oracle Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA), then you must first disable Oracle Database Vault.
Related Topics